
In the intricate landscape of digital interactions, a particular form of threat looms large, targeting the very essence of our personal sovereignty. This section delves into the strategies employed by nefarious actors to exploit human vulnerabilities, aiming not just at data but at the trust and openness that underpin our online engagements. Understanding these methods is crucial for fortifying our defenses and maintaining the integrity of our digital lives.
The Art of Exploitation: Often, the most effective invasions do not come through technological flaws but through the manipulation of our natural inclinations to trust and assist. This approach, known as deceptive persuasion, leverages social cues and psychological triggers to bypass traditional security measures. By appealing to our helpfulness or fear, these tactics can lead to unintentional disclosure of sensitive information.
Strategies for Resilience: To counteract these sophisticated maneuvers, it is essential to equip oneself with awareness and tools that enhance digital vigilance. This includes recognizing the signs of manipulative interactions, implementing robust verification practices, and fostering a mindset of cautious engagement online. By doing so, individuals can significantly reduce their susceptibility to these covert invasions, thereby protecting their digital footprints and personal autonomy.
Understanding Social Engineering Attacks

This section delves into the intricate dynamics that drive deceptive practices aimed at exploiting human vulnerabilities. By examining the underlying mechanisms of these tactics, we can gain a deeper understanding of why they are effective and how they can be countered.
The Psychology Behind Manipulation Tactics
Manipulative strategies often prey on basic human emotions and cognitive biases. For instance, the fear of missing opt out white pages or the desire for gain can be powerful motivators that cloud judgment. Attackers leverage these emotional triggers to create a sense of urgency or trust, which can lead to uncritical acceptance of their messages or requests.
Furthermore, the use of authority and credibility is a common tactic. By impersonating a figure of trust or authority, such as a bank official or a tech support agent, perpetrators can easily bypass initial skepticism. This psychological ploy capitalizes on the natural inclination to comply with figures perceived as authoritative or knowledgeable.
Another significant aspect is the exploitation of social bonds and community norms. Attackers may pose as friends or community members to gain access to sensitive information or to persuade individuals to perform certain actions. This approach not only leverages the trust inherent in social relationships but also plays on the fear of social exclusion if one does not comply with the perceived community expectations.
Understanding these psychological underpinnings is crucial for developing effective defenses against such manipulative practices. By recognizing the emotional and cognitive traps set by these tactics, individuals can better equip themselves to resist and report such attempts, thereby enhancing their overall security and resilience.
The Psychology Behind Manipulation Tactics
This section delves into the intricate strategies employed by individuals to influence others’ decisions and actions. Understanding these tactics is crucial for recognizing and mitigating their impact. We will explore common methods used to sway individuals, providing insights into the mechanisms behind these approaches.
| Technique | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Sending fraudulent messages designed to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information. | An email that appears to be from a legitimate bank asking for account details. |
| Pretexting | Creating a fabricated scenario to dupe someone into providing information or performing an action. | Pretending to be a colleague needing urgent access to confidential files. |
| Baiting | Offering something enticing in exchange for personal information or a favor. | Offering a free music download in exchange for completing a survey that asks for personal details. |
| Tailgating | Manipulating someone into allowing unauthorized access by appearing to have legitimate reasons. | Following an employee into a secure area by pretending to have forgotten an access card. |
| Scareware | Using fear tactics to make individuals purchase unnecessary or harmful software. | Pop-up messages claiming your computer is infected with viruses and offering a solution for purchase. |
Each of these techniques leverages specific psychological triggers such as urgency, fear, or trust. By understanding these triggers, one can better equip themselves to identify and counteract such manipulative tactics.
Common Techniques Used in Social Engineering

This section delves into the various methods employed by nefarious actors to deceive individuals and organizations. By understanding these tactics, one can better equip themselves against such deceptive practices. Here, we explore the most prevalent strategies used to exploit human vulnerabilities for illicit gains.
- Phishing: This technique involves the use of fraudulent communications that appear to come from a reputable source. The goal is often to steal sensitive data like credit card numbers and login information.
- Pretexting: In this scenario, the attacker fabricates a scenario (the pretext) to steal personal information or gain unauthorized access. They might impersonate a co-worker, police officer, or another individual with perceived authority.
- Baiting: This method lures victims with an item or service of perceived value. For example, offering free music downloads that are actually malicious software.
- Tailgating: Also known as “piggybacking,” this involves an unauthorized person following an employee into a restricted area. The attacker might claim to have forgotten their access card or badge.
- Quid Pro Quo: Here, the attacker offers a benefit in exchange for information. For instance, they might promise technical support in return for login credentials.
Each of these techniques leverages different aspects of human psychology, exploiting trust, curiosity, or urgency to achieve their objectives. Awareness of these methods is the first step in defending against them.
- Always verify the identity of the person or organization requesting sensitive information.
- Be cautious of unsolicited offers or communications that seem too good to be true.
- Implement strict access controls and educate employees about the risks of tailgating.
- Regularly update your knowledge about new and evolving tactics used by these deceptive actors.
By understanding and recognizing these common tactics, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to such deceptive practices, thereby enhancing their overall security posture.
Real-World Examples of Social Engineering Breaches
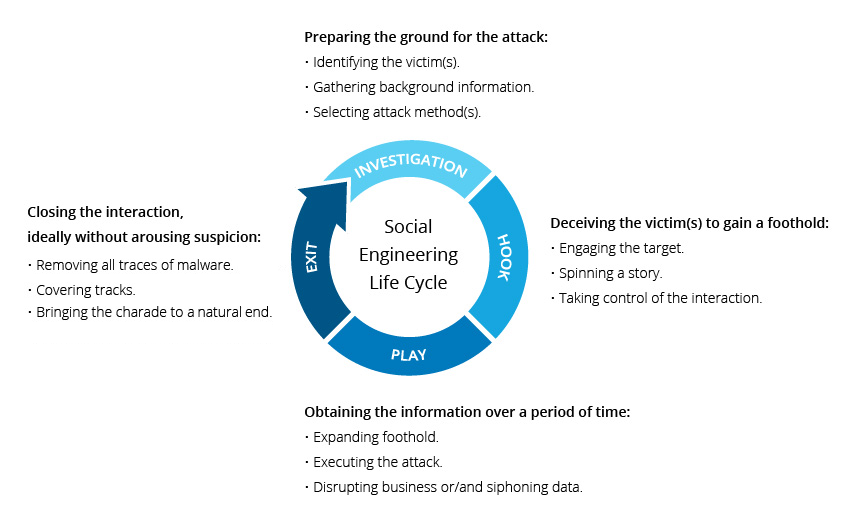
This section delves into concrete instances where deceptive practices have led to significant security lapses. By examining these cases, we gain insight into the tactics employed by fraudsters and the consequences they entail. Each example serves as a stark reminder of the importance of vigilance in safeguarding personal information.
- The Phishing Scandal of 2016: In this notable incident, a major corporation fell victim to an email scam. Employees were tricked into divulging sensitive data by emails that appeared to be from trusted sources within the company. This breach resulted in the leakage of confidential customer information, leading to widespread identity theft and financial loss.
- The Whaling Attack on a Financial Institution: A high-profile case involved a CEO impersonation, where the fraudsters targeted top executives with sophisticated emails requesting urgent fund transfers. The deception was so convincing that large sums of money were transferred to fraudulent accounts before the scam was detected.
- The Vishing Campaign Against a Tech Giant: Through voice phishing, scammers contacted employees posing as IT support staff, gaining access to internal systems. This breach exposed critical company data and disrupted operations significantly.
- The Tailgating Incident at a Defense Contractor: In this physical security breach, an unauthorized individual gained entry to a restricted area by closely following an employee through a secured door. This incident led to the theft of sensitive documents, highlighting vulnerabilities in physical security protocols.
These examples underscore the diverse methods used by perpetrators to exploit human vulnerabilities. They also emphasize the need for robust security measures and continuous employee training to mitigate such risks.
Understanding these real-world breaches not only helps in recognizing similar threats but also aids in developing effective strategies to prevent future occurrences. It is crucial for organizations and individuals alike to stay informed and vigilant to protect against these sophisticated deceptions.
Impact of Social Engineering on Online Privacy
In this section, we delve into the profound effects that deceptive practices can have on personal confidentiality in the digital realm. The strategies employed by malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities in human behavior can severely compromise the integrity of our digital identities and the security of our personal information.
Deceptive Tactics: Malicious individuals often use sophisticated ploys to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. These tactics range from impersonating trusted entities to crafting compelling narratives that trick users into revealing confidential details.
Impersonation and Phishing: One of the most prevalent methods involves impersonating legitimate organizations or individuals to deceive victims into providing login credentials, financial information, or other sensitive data. This not only jeopardizes the immediate victim but can also lead to widespread data breaches affecting numerous individuals.
Consequences of Breaches: When such breaches occur, the repercussions can be far-reaching. Personal information such as emails, passwords, and financial details can be exposed, leading to identity theft, financial loss, and a significant erosion of trust in digital platforms.
Long-term Effects: The impact of these breaches extends beyond immediate financial or identity theft risks. There is a psychological toll on victims, who may experience anxiety and a diminished sense of security when engaging in online activities. Moreover, the erosion of trust in digital services can hinder the adoption of beneficial technologies.
Understanding the mechanisms by which these breaches occur is crucial for developing effective countermeasures. By recognizing the signs of deception and implementing robust security practices, individuals and organizations can mitigate the risks associated with these manipulative strategies.
Strategies for Recognizing and Avoiding Manipulation
This section delves into effective methods to discern and evade deceptive practices that could compromise personal security. By understanding the tactics employed by manipulators, individuals can fortify their defenses and maintain a secure digital presence.
To effectively counter manipulation, it is crucial to recognize common signs and employ robust preventive measures. Here are several strategies to enhance your ability to detect and avoid such tactics:
- Awareness of Deceptive Communication: Be vigilant of unsolicited messages or calls that request sensitive information. Verify the identity of the sender or caller through independent means before responding.
- Secure Password Practices: Use complex, unique passwords for each account and consider employing a password manager to keep track of them securely.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA wherever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts, requiring not only a password but also a second form of verification.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all your devices and software updated to protect against known vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest tactics used by manipulators. Regularly read up on security blogs and updates from trusted sources.
- Use Secure Networks: Avoid accessing sensitive information over public Wi-Fi networks. If necessary, use a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt your data.
- Be Skeptical of Links and Attachments: Do not click on links or open attachments from unknown or suspicious sources. They could contain malware or lead to phishing sites.
- Review Privacy Settings: Regularly check and adjust the privacy settings on your social media and other online accounts to control who can access your information.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their vulnerability to manipulation and enhance their overall digital security. It is essential to remain proactive and vigilant in the face of evolving threats.
Best Practices for Enhancing Online Security
In this section, we delve into effective strategies to fortify your digital defenses. The focus is on proactive measures that can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, ensuring a safer digital environment for all users.
Implementing robust security practices is crucial in today’s digital age. Below is a comprehensive table outlining key actions that can be taken to enhance your online security:
| Practice | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Password Management | Use complex passwords and change them regularly. Consider using a password manager to keep track of them securely. | Prevents unauthorized access through weak or reused passwords. |
| Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) | Enable 2FA on all accounts where available. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification in addition to your password. | Significantly increases account security, even if passwords are compromised. |
| Regular Software Updates | Keep all software, including operating systems and applications, up to date. Updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities. | Reduces the risk of exploitation by cyber threats through outdated software. |
| Secure Browsing Habits | Be cautious of suspicious links or emails. Use secure and reputable websites for transactions. | Helps avoid phishing scams and malware infections. |
| Data Encryption | Use encryption tools to protect sensitive data both at rest and in transit. | Ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the decryption key. |
By adhering to these practices, users can significantly enhance their digital security posture, mitigating risks associated with cyber threats and ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of their digital interactions.
Resources for Further Learning and Protection
Introduction: This section aims to provide a comprehensive list of materials and tools that can assist individuals in deepening their understanding and fortifying their defenses against deceptive practices prevalent in the digital realm. By exploring these resources, one can enhance their awareness and develop robust strategies to safeguard personal information.
Educational Platforms: Numerous online platforms offer courses and tutorials that delve into the intricacies of digital security. Websites like Coursera and Udemy provide specialized courses that cover various aspects of cybersecurity, including methods to identify and thwart fraudulent activities.
Government and Industry Resources: Government agencies such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and the National Cyber Security Alliance (NCSA) offer valuable insights and guidelines on maintaining security in the digital space. Their websites are rich sources of information, including tips on how to avoid scams and protect sensitive data.
Books and Publications: For those who prefer a more traditional learning approach, there are numerous books available that explore the strategies used by fraudsters and provide countermeasures. Titles like “The Art of Deception” by Kevin Mitnick offer deep insights into the minds of manipulators and how to protect against their tactics.
Support Groups and Forums: Online communities and forums, such as those found on Reddit or dedicated cybersecurity websites, can be invaluable. These platforms allow users to share experiences, ask questions, and learn from others who have faced similar challenges. Participation in these groups can provide real-world advice and support.
Software and Tools: There are various software solutions and tools designed to enhance digital security. Anti-malware programs, VPNs, and password managers are essential tools that can help in securing personal information and preventing unauthorized access.
By utilizing these resources, individuals can significantly bolster their defenses against the deceptive practices that threaten their digital safety. Continuous learning and proactive measures are key to maintaining a secure online presence.