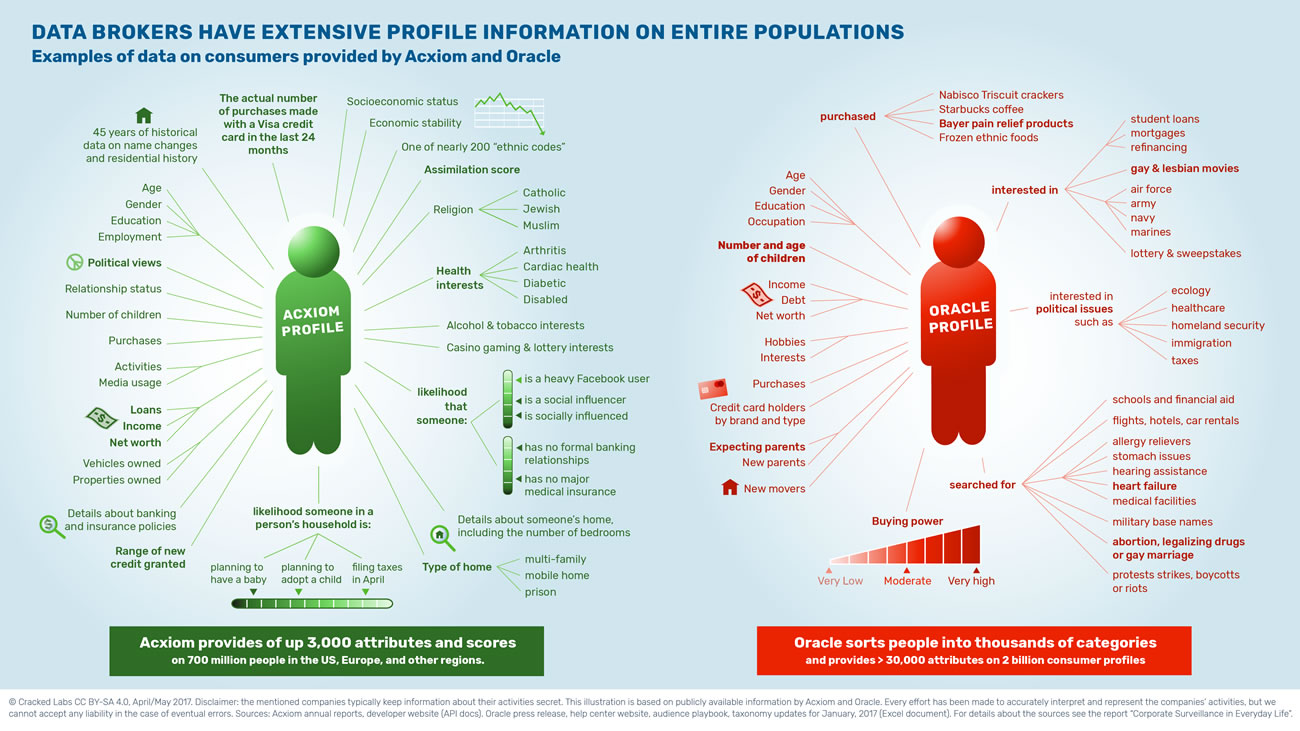
In the vast digital landscape, where every click and scroll is tracked, a silent yet powerful industry operates behind the scenes. This industry, often overlooked, plays a crucial role in shaping the way businesses connect with potential customers. By gathering and analyzing vast amounts of personal information, these entities enable advertisers to target their audience with unprecedented precision.
The intricate mechanisms of this sector are fascinating. Information aggregators collect data from various sources, ranging from social media interactions to online shopping habits. This data is then meticulously processed and categorized, allowing for highly tailored marketing strategies. The impact of these practices on consumer behavior and market dynamics is profound, yet often subtle.
Moreover, the ethical implications of such data collection and utilization are significant. As these aggregators continue to refine their methods, the balance between privacy and personalized marketing becomes increasingly delicate. Understanding the operations and consequences of this industry is essential for both consumers and businesses in navigating the digital age.
In this section, we delve deeper into the workings of information aggregators, exploring their methodologies, the technologies they employ, and the broader implications of their activities. Through this exploration, we aim to shed light on the complex interplay between technology, marketing, and individual privacy.
Understanding Data Brokers
This section delves into the pivotal role that entities play in the realm of marketing, particularly through the collation and utilization of extensive information sets. These entities, often overlooked, are instrumental in shaping the landscape of promotional strategies, yet their operations and contributions are not always transparent.
In the digital age, the aggregation of information has become a cornerstone for enhancing the precision and effectiveness of promotional efforts. By gathering and analyzing vast arrays of personal details, these entities enable marketers to tailor their messages more effectively to specific demographics. This process not only optimizes the reach of promotional content but also significantly boosts its relevance to the intended audience.
The mechanisms through which these entities collect and synthesize information are complex and multifaceted. They range from the analysis of public records and social media activity to more sophisticated techniques involving artificial intelligence and machine learning. These advanced technologies allow for the extraction of patterns and trends that would be otherwise invisible to the human eye, thereby enhancing the depth and accuracy of the insights provided.
Moreover, the role of these entities extends beyond mere collection and analysis. They also play a critical part in the dissemination of promotional materials, ensuring that these reach the right audience at the right time. This targeted approach not only maximizes the impact of marketing campaigns but also reduces waste by avoiding the broadcast of irrelevant messages to uninterested parties.
In conclusion, while often operating behind the scenes, these entities are indispensable in the modern marketing ecosystem. Their ability to aggregate and leverage vast amounts of information not only drives efficiency in promotional efforts but also sets the stage for more personalized and effective communication strategies.
Role of Data Aggregation in Advertising
Data aggregation plays a pivotal role in the modern advertising landscape. By compiling and analyzing vast amounts of information, companies can tailor their marketing strategies to meet specific consumer needs and preferences. This section delves into the significance of consolidating diverse sets of information and how it enhances the effectiveness of promotional efforts.
The process of aggregating information involves gathering data from various sources and integrating it into a comprehensive dataset. This consolidated view allows marketers to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that would be difficult to discern from individual data points alone. For instance, by combining purchase history, browsing behavior, and demographic details, advertisers can create highly targeted campaigns that resonate with particular segments of the audience.
Moreover, data aggregation enables the creation of detailed consumer profiles, which are instrumental in personalizing advertising content. These profiles help in predicting consumer behavior and preferences, thereby allowing advertisers to deliver more relevant and engaging messages. The result is a more efficient use of marketing resources and a higher likelihood of converting prospects into customers.
However, the effectiveness of data aggregation in advertising is not without challenges. The integration of multiple data sources requires sophisticated analytical tools and expertise to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the insights generated. Additionally, there is the constant need to update and refine the data to keep pace with changing consumer behaviors and market dynamics.
In conclusion, data aggregation is a critical component of contemporary advertising strategies. It empowers advertisers to make informed decisions, tailor their messages to specific audiences, and ultimately drive better business outcomes. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of data aggregation will likely become even more integral to the success of marketing campaigns.
Privacy Concerns Raised by Data Brokers
This section delves into the intricate issues surrounding the collection and utilization of personal information by intermediaries in the digital marketplace. As these entities gather vast amounts of sensitive data, the implications for individual privacy are profound and multifaceted.
The primary concern revolves around the extent to which these intermediaries can access and use personal details without explicit consent. Here are some key areas of contention:
- Surveillance: Continuous tracking of user activities across various platforms raises questions about the boundaries of acceptable monitoring.
- Data Mining: Extensive analysis of personal data to predict consumer behavior can lead to intrusive marketing strategies.
- Security Risks: The potential for data breaches exposes individuals to risks of identity theft and financial fraud.
- Transparency: Lack of clear information about data collection practices can undermine user trust and awareness.
Moreover, the integration of collected information into targeted promotional campaigns further exacerbates these privacy issues. The following points highlight the specific challenges:
- Selective Targeting: Personalized ads based on detailed user profiles can feel invasive and manipulative.
- Data Accuracy: Inaccurate information used for targeting can result in inappropriate or offensive content being directed at individuals.
- Consent and Control: Users often have limited ability to opt out of data collection or to manage how their information is used.
Addressing these concerns requires a comprehensive approach that includes regulatory measures, technological safeguards, and enhanced consumer education. Balancing the benefits of personalized marketing with the fundamental right to privacy remains a critical challenge in the digital age.
Impact of Data Brokers on Targeted Ads

This section delves into the profound effects that entities specializing in the collection and sale of consumer information have on the precision and effectiveness of promotional messages directed at specific audiences. These entities play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of personalized marketing, often determining which advertisements consumers encounter based on their browsing habits and demographic details.
Enhancing Precision: By aggregating vast amounts of user data, these entities enable advertisers to refine their targeting strategies significantly. This precision leads to higher conversion rates as ads are more likely to resonate with the intended audience, thereby increasing the return on investment for advertisers.
Economic Implications: The ability to target ads more effectively has substantial economic benefits. It allows businesses to allocate their marketing budgets more efficiently, focusing on segments that are most likely to engage with their products or services. This efficiency not only boosts individual business performance but also contributes to the overall economic productivity by optimizing resource allocation.
Consumer Experience: While targeted ads can be beneficial in providing consumers with offers that match their interests, they also raise concerns about privacy and the potential for over-exposure to marketing messages. The balance between providing a personalized consumer experience and respecting privacy boundaries is a delicate one, requiring careful consideration and regulation.
Market Dynamics: The involvement of these entities in the advertising process has reshaped market dynamics, particularly in competitive industries. Companies that effectively leverage targeted advertising through these entities can gain a significant edge over competitors who do not, potentially altering the competitive landscape and consumer perceptions.
In conclusion, the role of entities that facilitate the collection and sale of consumer data in targeted advertising is multifaceted, impacting not only the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing strategies but also the broader economic and consumer landscapes. As the digital marketing ecosystem continues to evolve, understanding these impacts will be crucial for both businesses and policymakers.
Regulatory Challenges for Data Brokers
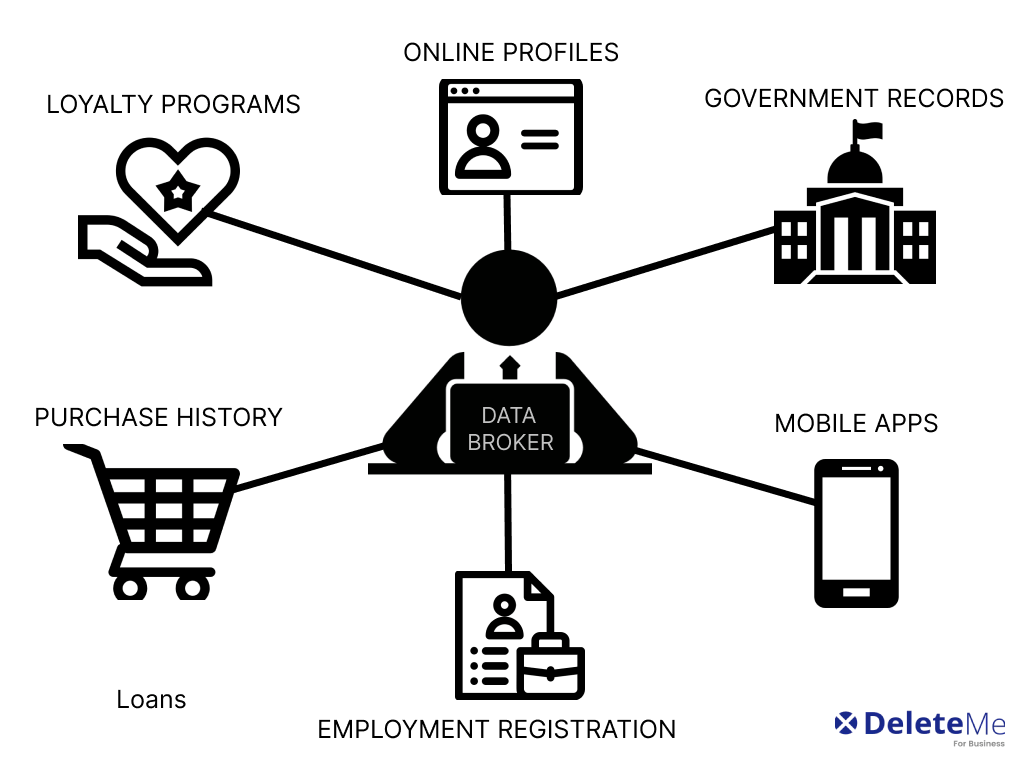
This section delves into the complex landscape of legal and regulatory hurdles faced by entities that gather and sell consumer information. As these organizations operate across various jurisdictions, they must navigate a patchwork of laws designed to protect consumer rights and privacy.
Compliance with Multiple Jurisdictions
One of the primary challenges is the need to comply with a multitude of regulations across different countries and states. Each jurisdiction may have unique requirements regarding the collection, storage, and use of personal information. This fragmented regulatory environment necessitates constant adaptation and meticulous attention to detail.
Evolving Privacy Laws
Privacy laws are continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and increasing public awareness. Entities must stay abreast of legislative changes, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which imposes stringent requirements on the handling of personal data. Adapting to these changes requires significant resources and expertise.
Balancing Commercial Interests with Privacy Rights
Regulators aim to strike a balance between enabling commercial activities and safeguarding individual privacy. This delicate equilibrium poses a challenge for organizations, as they must demonstrate that their practices are both profitable and compliant with privacy standards. Demonstrating this balance can be complex and requires a clear understanding of both legal requirements and ethical considerations.
Enforcement and Penalties
The potential for significant penalties for non-compliance adds another layer of complexity. Regulators have the authority to impose hefty fines for violations, which can be detrimental to an organization’s financial health. Therefore, ensuring compliance is not only a matter of legal necessity but also a critical component of risk management.
Public Perception and Trust
Lastly, the public’s perception of these organizations plays a crucial role in regulatory challenges. As consumer awareness grows, so does the scrutiny of their practices. Building and maintaining trust with the public is essential, as it can influence regulatory outcomes and public policy.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for entities that collect and sell consumer information is fraught with challenges. Navigating these challenges requires a comprehensive understanding of legal requirements, a commitment to ethical practices, and a proactive approach to compliance.
Techniques Data Brokers Use to Collect Data
Understanding the Methods of Information Gathering
In the digital realm, entities that compile and sell personal details employ a variety of tactics to amass comprehensive profiles on individuals. This section delves into the methodologies these entities utilize to collect such information, shedding light on the processes that fuel the personalized marketing industry.
Cookies and Tracking Technologies
One of the primary tools in the arsenal of information collectors is the use of cookies and similar tracking technologies. These small files, stored on users’ devices, monitor browsing habits, recording the websites visited and the actions taken therein. This data is then aggregated to create detailed user profiles, which are instrumental in delivering tailored content and advertisements.
Social Media Mining
Another significant source of personal information is social media platforms. Entities that compile and sell personal details often tap into the vast reservoirs of data shared publicly by users on these platforms. By analyzing posts, likes, comments, and even private messages, these entities can glean insights into personal preferences, relationships, and behaviors.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Direct methods of data collection also play a crucial role. Surveys and questionnaires, often embedded within websites or distributed via email, solicit personal information from users in exchange for incentives such as discounts or free content. While these methods require user consent, they are nonetheless effective in gathering detailed personal data.
Transactional Data Analysis
Entities that compile and sell personal details also scrutinize transactional data from various online platforms. By analyzing purchase histories, subscription details, and other transactional information, these entities can infer a wealth of personal information, including financial status, shopping preferences, and lifestyle choices.
Mobile App Data Collection
With the proliferation of smartphones, mobile applications have become a rich source of personal information. Many apps request permissions to access device features such as the camera, microphone, and location services. These permissions enable entities to collect data on user behavior, location history, and even conversations, contributing to comprehensive user profiles.
Conclusion
The techniques employed by entities that compile and sell personal details are diverse and sophisticated. From tracking technologies to social media mining, each method plays a crucial role in building detailed profiles that drive personalized marketing strategies. Understanding these techniques is essential for consumers to make informed decisions about their online presence and privacy.
Consumer Awareness and Information Collectors
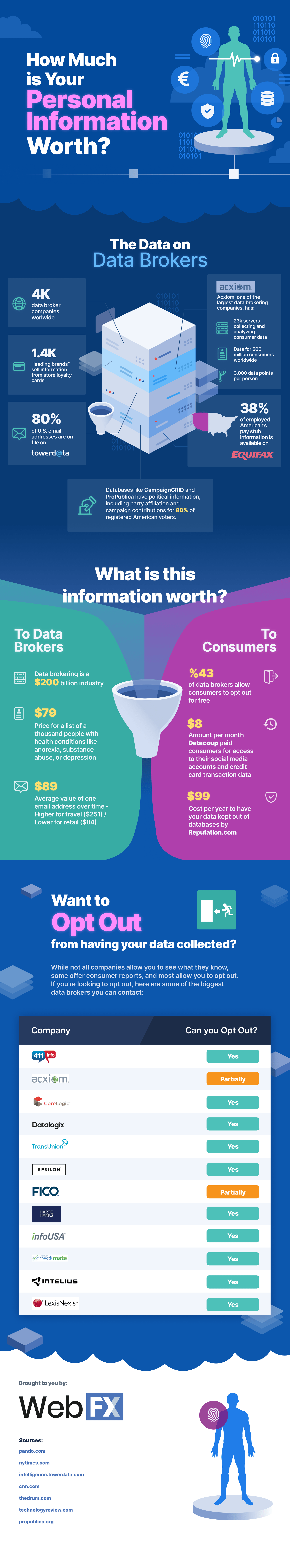
This section delves into the growing consciousness among individuals regarding the practices of entities that gather and manage personal information. As these entities play a pivotal role in shaping marketing strategies, understanding their operations and the implications for privacy is crucial.
Increasing Transparency Demands: Consumers are increasingly demanding more transparency from information collectors. They seek to understand what details are being gathered, how they are used, and with whom they are shared. This shift in consumer attitude is driven by a realization of the value of personal information and its impact on privacy and security.
Educational Initiatives: Various organizations and regulatory bodies are launching educational campaigns to inform the public about the activities of information collectors. These initiatives aim to empower consumers with knowledge, enabling them to make informed decisions about their online interactions and the sharing of personal data.
Impact on Business Practices: The heightened awareness among consumers is prompting information collectors to reassess their strategies. Businesses are now more focused on developing ethical data collection practices and ensuring compliance with privacy laws, which not only protects consumer rights but also enhances brand reputation.
Technological Solutions: To address consumer concerns, innovative technologies are being developed that offer more control to users over their personal information. These solutions include advanced privacy settings, data management tools, and encryption methods, all designed to safeguard personal information from unauthorized use.
Future Outlook: As awareness continues to grow, the relationship between consumers and information collectors is expected to evolve. This evolution will likely lead to more balanced and mutually beneficial interactions, where the rights and preferences of consumers are respected and protected.
Future Trends in Data Brokerage
![]()
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the role of intermediaries who facilitate the exchange of information is poised for significant transformation. This section explores emerging directions that could redefine How to get off BlockShopper these entities operate and the implications for various stakeholders.
Advancements in Technology: The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is expected to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of information processing. These technologies will enable more sophisticated analyses and predictive models, potentially leading to more personalized marketing strategies.
Regulatory Shifts: With growing concerns over privacy and data protection, there is a likelihood of stricter regulations globally. These changes could necessitate new compliance measures and operational adjustments, affecting the business models of information intermediaries.
Consumer Empowerment: There is a trend towards greater consumer awareness and control over personal information. Tools and platforms that allow users to manage and opt out of information sharing are likely to become more prevalent, influencing the strategies of information facilitators.
Ethical Considerations: The industry is increasingly recognizing the importance of ethical practices in information handling. This includes transparency in operations, fair usage policies, and ensuring that benefits from information exchange are equitably distributed.
Globalization and Localization: The need to cater to diverse markets with unique cultural and legal contexts will drive innovations in how information is collected and utilized. This could involve developing tailored solutions that respect local norms and regulations.
In conclusion, the future of information intermediation is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, evolving regulations, and heightened consumer expectations. Balancing innovation with ethical considerations and compliance will be crucial for sustained success in this dynamic field.
Balancing Profit and Privacy in Data Brokering
In the realm of digital marketing, the collection and utilization of user information have become pivotal for business success. However, this practice often clashes with the fundamental rights to privacy. This section delves into the intricate balance between generating revenue and safeguarding personal privacy, exploring strategies and ethical considerations that companies must navigate.
To effectively manage this delicate equilibrium, several approaches can be adopted:
- Transparent Practices: Companies should openly communicate their methods of information collection and usage to users. This transparency not only builds trust but also ensures that users are aware of how their data is being handled.
- Consent-Based Models: Prioritizing user consent is crucial. Users should have the option to opt-in or opt-out of data collection processes, and their preferences should be respected and enforced.
- Anonymization Techniques: Employing methods that obscure personal identifiers from collected information can significantly reduce privacy risks while still allowing for valuable insights to be derived.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to local and international laws and regulations related to data protection is non-negotiable. This includes staying updated on changes in legislation and adjusting practices accordingly.
- Ethical Decision-Making: Beyond legal requirements, companies should adopt a moral framework that prioritizes user privacy over short-term gains. This involves making decisions that are in the best long-term interest of both the company and its users.
Implementing these strategies not only helps in maintaining a balance between profitability and privacy but also enhances the company’s reputation and user loyalty. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, these practices will become increasingly essential for sustainable business growth.